Omega 3 and Children
Life seems to be a constant hustle and bustle with kids, and their diets tend to suffer. School lunches are get poor grades, and we eat more fast and processed foods. As hard as we try to feed our kids healthy foods, they are still lacking one very vital nutrient — Omega 3 Fatty Acids. As parents, we must understand the importance of omega 3 for children and make sure they are getting enough.
It’s hard these days to feed kids a healthy diet when TV commercials advertise foods that are less than par. The store shelves are lined at kid’s eye levels with processed foods that contain little or no valuable nutrition and school lunches come from mostly cans. We have a tough fight ahead of us!
 One very important point we cannot miss is that researchers are finding that Omega 3 Fatty Acids are a basic building block of brain cells. Kids need healthy brain cells for learning. Omega 3 can reduce symptoms of ADHD, childhood depression, and even asthma. The studies are ongoing and researchers are finding some very positive results with the use of Omega 3.
One very important point we cannot miss is that researchers are finding that Omega 3 Fatty Acids are a basic building block of brain cells. Kids need healthy brain cells for learning. Omega 3 can reduce symptoms of ADHD, childhood depression, and even asthma. The studies are ongoing and researchers are finding some very positive results with the use of Omega 3.
If you’re pregnant, make sure you get adequate Omega 3 in order to build healthy fetal brain cells. Infants who use formula need formula enriched with Omega 3, while young children also need to eat foods high in this nutrient. Many supplements for pregnant women, infants, and children are enriched with added Omega 3.
Omega 3 and Safety for Children
The highest levels of Omega 3 in food comes from fish and fish oils. The problem with high amounts of fish in the diet is the possible high intake of mercury. High mercury fish are: tuna, swordfish, king mackerel, and orange roughy. Tuna has the highest levels of mercury and is commonly used to make sandwiches for kids. Recommendations for tuna in kids’ diets is three ounces weekly. That is about ½ a can of tuna. This issue can add to the deficiency of Omega 3 fatty acids.
 Best fish for kids are ones that swim in cold water and are wild caught. This includes; tilapia, cod, salmon, and shrimp. While these are generally fatty fish, they have way less mercury. If your child is vegetarian or refuses to eat fish, there are healthy vegetarian sources including: flax and flax products, soybeans, canola oil, and walnuts (make sure your child does not have a tree nut allergy if you choose to use walnuts). An easy way to get your child to eat these foods is to use them in foods like: oatmeal sprinkled with flax powder, or to bake up some flax muffins with canola oil.
Best fish for kids are ones that swim in cold water and are wild caught. This includes; tilapia, cod, salmon, and shrimp. While these are generally fatty fish, they have way less mercury. If your child is vegetarian or refuses to eat fish, there are healthy vegetarian sources including: flax and flax products, soybeans, canola oil, and walnuts (make sure your child does not have a tree nut allergy if you choose to use walnuts). An easy way to get your child to eat these foods is to use them in foods like: oatmeal sprinkled with flax powder, or to bake up some flax muffins with canola oil.
You can always try a children’s Omega 3 supplement. There are many types of children’s multi-vitamins that already contain Omega 3. There are even children’s fish oil capsules. If you do use the children’s fish oil supplement, check the label to see if the brand is low mercury. Make sure you check with your child’s doctor before using an Omega 3 supplement.
Omega 3 Dosage For Kids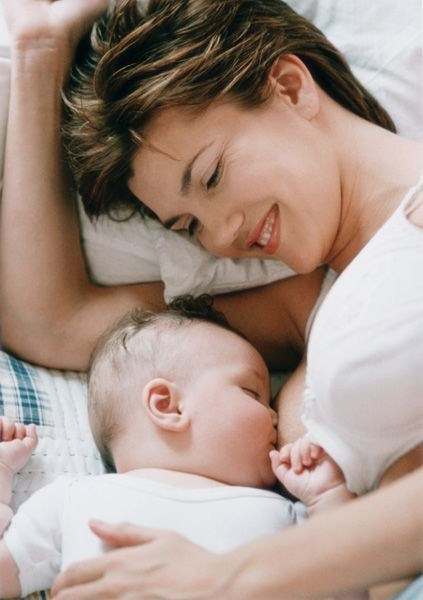
The best way for kids to get adequate amounts of Omega 3 is to have them eat 2 to 3 servings of fish that is “low mercury” a week. Children do not need as much as adults to get the health benefits. If you choose to use a supplement, infants need about 300mg to 500 mg Omega 3 every day. Infants who breastfeed will get enough Omega 3 from breast milk as long as you eat enough “low-mercury” foods containing Omega 3. Make sure that during pregnancy and breastfeeding you are not eating sources of mercury. Infants who bottle feed should take a formula fortified with Omega 3. Check labels carefully, but most are now fortified.
If your child will not eat fish, ask their pediatrician about an Omega 3 supplement. The recommended dosage for younger children is 600 mg Omega 3 every day. If you can get your child to eat fish, all they need is about 3 to 6 ounces of salmon or whitefish two times a week. The recommended amount for older children and teenagers is right around 1,600mg daily.
If you have a young child with ADHD (Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder), depression, or autism, the recommended dosage is 1,000mg daily. Always consult with a doctor before giving Omega 3 to a young child and only use higher doses under close supervision. It is generally safe for kids and side-effects are mild if given with food.
Conclusion
Understanding the importance of adequate omega 3 for children helps them grow and develop as healthy children and adults. Omega 3 can help brain development, as well as help prevent certain health conditions. Studies are ongoing to see if Omega 3 can help reduce the symptoms of ADHD, Autism, and childhood depression. Omega 3 can be supplemented, but the best source for kids is a healthy diet with “low mercury” Omega 3 foods.
TOP 5
OMEGA3Supplements |
|||||
| Omega3 Premium | Dr. Sears OmegaRx | Purity Products | Nordic Naturals | Nature Made | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| Price (1 bottle) Price (4 bottles)(*best value) |
$49.95 $138.00 |
$50.95 $305.70 |
$46.95 $281.70 |
$69.95 $419.70 |
$25.95 $155.70 |
| Overall Rating | 99.85% | 89.20% | 82.60% | 76.30% | 72% |
| Effectiveness |





|





|





|





|





|
| Speed of Results | Extremely Fast | Good | Average | Average | Slow |
| Quality of Ingredients | Premium | Good | Good | Average | Unknown |
| Customer Satisfaction Evaluation | 99.40% | 84% | 79%% | 72%% | 61%% |
| Safety Evalutation | Safe for Use | Safe for Use | Safe for Use | Safe for Use | Safe for Use |
| Customer Service Rating |





|





|





|





|





|
| Reorder Rate | Highest | Good | Good | Average | Average |
| Return Policy | Risk Free | Risk Free | Risk Free | No guarantee | Unclear |
| Success Rate | 99.40% | 81.10% | 74% | 71.20% | 62% |

 Subscribe Now
Subscribe Now